The articles are notes I took on the SQL Tutorial - Full Database Course for Beginners course.
They break into four parts:
- First article will introduce what is a database, SQL, keys and walk through the installation of MySQL on Mac.
- Second article introduces the common SQL data types, basic query syntax …etc.
- In third article we will create company tables, practice how to query on data, and introduce Functions, Wildcards …etc.
- The last article we introduce ER Diagrams, a way to diagram the requirements into figures, then we learn how to transform the ER Diagrams into actual SQL table schemas.
Now, let’s get started.
TL:DR
- Data types in MySQL
- Create, Delete and Alter Table schema
- Insert and Select Data
- Data constraints
- Data comparison options
- Update & Delete
- Basic Queries
- References
Data types in MySQL
1INT 2// integers, numbers without decimal 3 4DECIMAL(M,N) 5// numbers with floating 6// Maximum total digits 7// Maximum total digits after decimal point 8 9VARCHAR(l) 10// String of text of maximum length of l 11// need to be wrapped in single quote '' 12 13BLOB 14// Binary large object, stores large data 15// ususally store images or files 16 17DATE 18// 'YYYY-MM-DD' 19 20TIMESTAMP 21// 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'
Create, Delete and Alter Table schema
-
Create table
Let’s write our first query: create the first table inside database
giraffe:1CREATE TABLE student ( 2 student_id INT PRIMARY KEY, 3 name VARCHAR(20), 4 major VARCHAR(20), 5); 6 7// or you can specify PRIMARY KEY in this way: 8CREATE TABLE student ( 9 student_id INT, 10 name VARCHAR(20), 11 major VARCHAR(20), 12 PRIMARY KEY(student_id) 13); -
Delete table
1DROP TABLE student; -
Alter table schema ( add or delete column )
1// add column 2ALTER TABLE student ADD gpa DECIMAL(3, 2); 3 4// delete column 5ALTER TABLE student DROP COLUMN gpa; 6 -
Describe table schema ( print table schema )
1DESCRIBE table_name;
Insert and Select Data
-
insert row data
1// insert with all fields 2INSERT INTO student VALUES(1, 'John', 'history'); 3 4// insert with certain fields (others assign to null) 5INSERT INTO student(student_id, name) VALUES(2, 'Alex');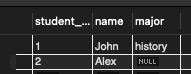
-
select (print) table data
1SELECT * FROM student;
Data constraints
-
Not Null
1CREATE TABLE student ( 2 // ..., 3 major VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, 4); -
Unique
Note that Primary Key is actually the combination of
NOT NULLandUNIQUE1CREATE TABLE student ( 2 // ..., 3 major VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE, 4); -
Default
1CREATE TABLE student ( 2 // ..., 3 major VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'undecided', 4); -
Auto Increment
If the data type is
INT, we can use theAUTO_INCREMENTconstraint1CREATE TABLE student ( 2 student_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, 3 // ... 4);
Data comparison options
1// equals 2A = B 3 4// not equals 5A <> B 6 7// greater than 8A > B 9 10// less than 11A < B 12 13// greater than or equal to 14A >= B 15 16// less than or equal to 17A <= B
Update & Delete
-
Update all rows
1// update "one" column 2UPDATE student 3SET major = 'Chinese'; 4 5// update "multiple" columns 6UPDATE student 7SET major = 'Chinese', gpa = '3.8'; -
Update rows that match certain condition
1// basic 2UPDATE student 3SET major = 'Chinese' 4WHERE name = 'Alex'; 5 6// OR 7UPDATE student 8SET major = 'Chinese' 9WHERE name = 'Alex' OR name = 'alex'; 10 11// AND 12UPDATE student 13SET major = 'Chinese' 14WHERE name = 'Alex' AND major = 'CH'; -
Delete all rows
1DELETE FROM student; -
Delete rows that match certain condition
1DELETE FROM student 2WHERE student_id = 1;
Basic Queries
-
Select All
1SELECT * FROM student; -
Select certain column
1SELECT student.major FROM student; -
Order by
1// order by data with INT or DECIMAL, default to ascending 2SELECT student.major FROM student 3ORDER BY student_id; 4 5// order other kinds of data, eg: VARCHAR 6SELECT student.major FROM student 7ORDER BY name; // alphabetical order 8 9// ascending (default) 10SELECT student.major FROM student 11ORDER BY student_id ASC; 12 13// descenging 14SELECT student.major FROM student 15ORDER BY student_id DESC; 16 17// order by multiple columns 18SELECT student.major FROM student 19ORDER BY major, student_id DESC; 20// order first by major, then student_id in DESC -
Limit
1// show only 2 rows 2SELECT * FROM student 3LIMIT 2; 4 5// combine with WHERE and ORDER BY 6SELECT * FROM student 7WHERE student_id < 3 8ORDER BY student_id DESC 9LIMIT 2; -
In (chain of or)
1// IN & AND 2SELECT * FROM student 3WHERE name IN ('Alex', 'Allen');
Reference
- SQL Tutorial - Full Database Course for Beginners