The articles are notes I took on the SQL Tutorial - Full Database Course for Beginners course.
They break into four parts:
- First article will introduce what is a database, SQL, keys and walk through the installation of MySQL on Mac.
- Second article introduces the common SQL data types, basic query syntax …etc.
- In third article we will create company tables, practice how to query on data, and introduce Functions, Wildcards …etc.
- The last article we introduce ER Diagrams, a way to diagram the requirements into figures, then we learn how to transform the ER Diagrams into actual SQL table schemas.
Now, let’s get started.
TL:DR
- What is a Database
- Tables and Keys
- SQL introduction
- Install MySQL on Mac
- Reference
What is a Database
- Database is any collection of related information
- Database Management Systems (DBMS) make it easy to create, maintain and secure a database
- DBMS allow you to perform the C.R.U.D. operations and other administrative tasks
- Two types of Databases: Relational & Non-Relational
- Relational databases use SQL and store data in tables with rows and columns, eg: MySQL
- Non-Relational databases store data using other data structures, eg: JSON
Tables and Keys
Table
A table is consist of columns and rows:
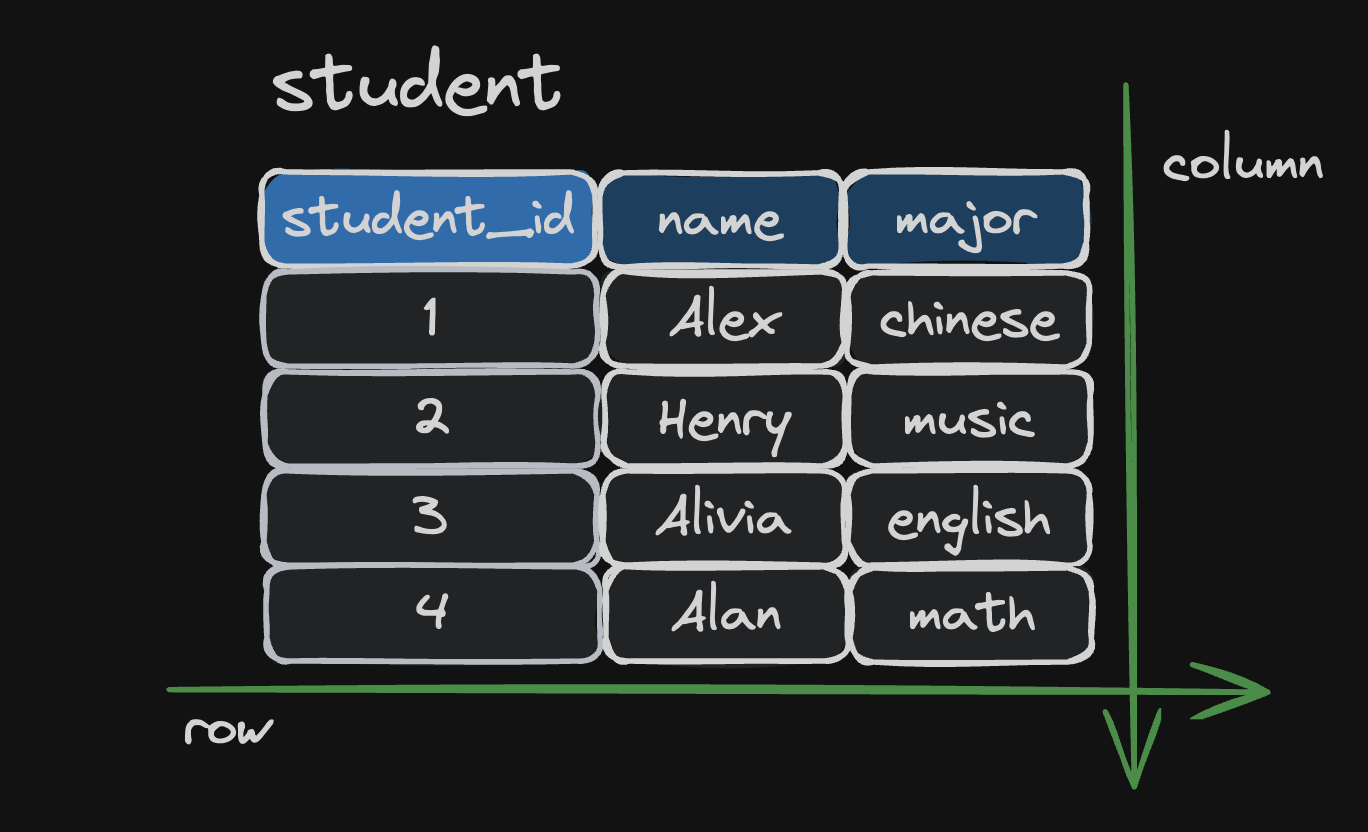
Keys
-
Primary Key
-
Attribute uniquely defines the row in the table / database
-
Must be unique
-
Can be anything, number, string …etc
-
Real World Related
-
surrogate key
No mapping to the real world, doesn’t mean anything, ie: random unique numbers.
-
natural key
Means something in the real world, ie: social security number.
-
-
for example: column
branch_idis the Primary Key of the table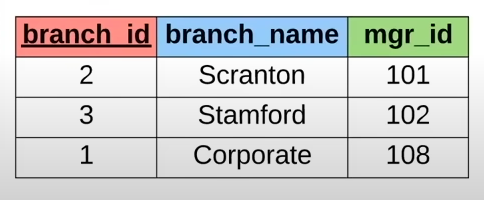
-
-
Foreign Key
- usually is the Primary Key of another table, providing a way to define relationships between 2 tables, eg: table
Employeehas a Foreign Keybranch_id, which is the Primary Key of theBranchtable - it can also be from the same table, eg:
super_id(Foreign Key) is theemp_idfrom the same tableEmployee
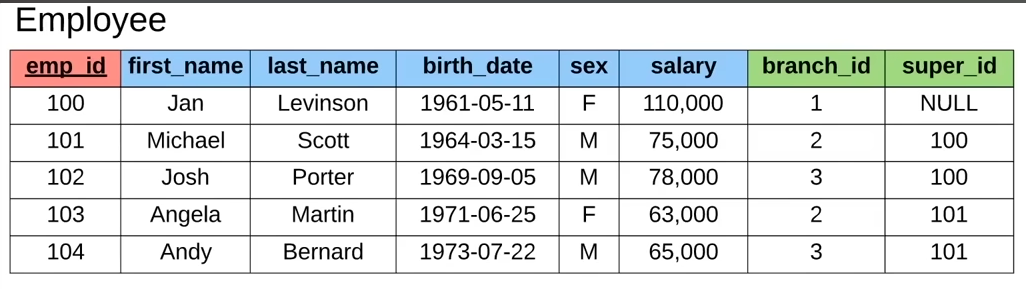

- usually is the Primary Key of another table, providing a way to define relationships between 2 tables, eg: table
-
Composite Key
-
Primary Key is a composite of 2 columns
-
for example: the Primary Key below is composite of
branch_idandsupplier_name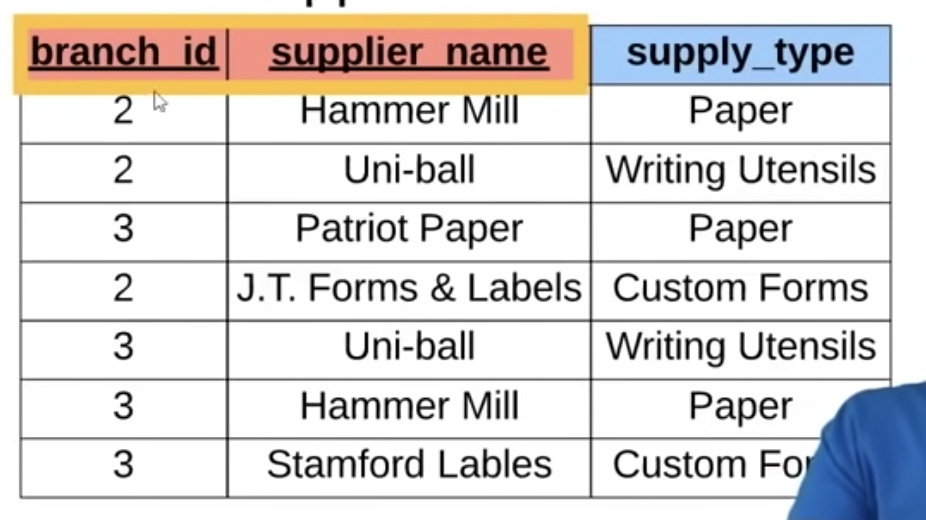
-
composite key can also be Foreign Key, eg: the
emp_idandclient_idfrom theWorks_Withtable is the also Foreign Keys, which is the Primary Keys ofEmplayeetable andClienttable


-
SQL introduction
What is SQL
- SQL (Structure Query Language) is a language used for interacting with RDBMS (Relational Database Management System)
- you can use SQL to tell RDBMS to do things for you:
- create / manage db
- design / create db tables
- CRUD
- It’s a language that mashes the below 4 types of languages:
- Data Query Language (DQL)
- query the db for information
- get information (R)
- Data Definition Language (DDL)
- define db schemas
- Data Control Language (DCL)
- user & permission management
- Data Manipulation Language (DML)
- insert (C), update (U), delete (D) data from db
- Data Query Language (DQL)
What is Query
-
Query is a set of instruction to tell RDBMS the information you want it to retrieve for you, for example:
1SELECT employee.name, employee.age # select what column 2FROM employee # from which table 3WHERE emplyee.salary > 30000; # conditions
Install MySQL on Mac
-
Download MySQL
Go to this website, click
macOS 13 (ARM, 64-bit), DMG Archiveto download, if your mac is intel chip, clickmacOS 13 (x86, 64-bit), DMG Archiveinstead. -
remember the
user,addressand thepasswordyou set, we will have to use it to connect to our local database server. -
start our MySQL server on our computer
-
allow bash / zsh to use
mysqlcommandRun this in the terminal first
1export PATH=${PATH}:/usr/local/mysql/bin/Then run this:
1source ~/.zshrc # If you use Oh-My-Zsh 2 3# or, if you use Default Bash, run this instead 4source ~/.bashrc -
login to mysql local server
Now the
mysqlcommand should be activated. But when you entermysqlcommand inside terminal, you will see this:1$ mysql 2ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'YOUR_COMPUTER_USERNAME'@'localhost' (using password: NO)It is saying we should type in password in order to login to our MySQL server:
1$ mysql -u root -p # hit enter 2Enter password: # type in password and you will be logged in 3 4# ... 5 6mysql> # you can start typing your MySQL command -
Create our first database
1mysql> create database YOUR_DB_NAME; 2# don't forget the ";" to finish the command -
Download MySQL Workbench
It is totally fine to use terminal to give MySQL commands, but we will use MySQL Workbench instead, it is a visualized editor for MySQL, providing us better DX.
Download the app from this link.
After installation, login to the Local instance 3306 with the password you set.
After login, you shall see the database you just created inside scheme, for my case, it’s
giraffe:
-
Appendix
-
How to exit inside terminal
type
exitto exit the mysql server -
If you wanna alter your MySQL server password inside terminal
1mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'YOUR_NEW_PASSWORD';
-
Reference
- SQL Tutorial - Full Database Course for Beginners
- How to fix "command not found: mysql" in Zsh